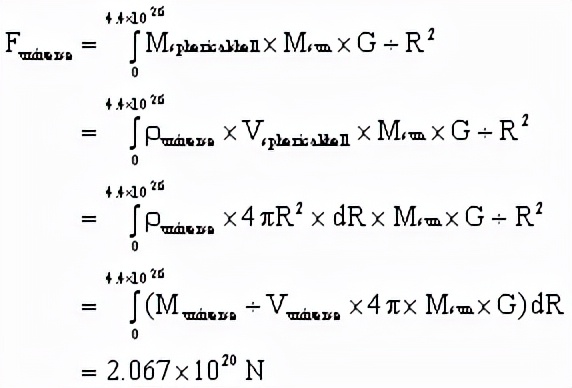作者: 愛霞
近日,學者王行洪先生髮表了一篇物理.學論文。論文中研究了在太陽系中,宇宙射線的加速問題。研究的結論,從根本上否定了狹義相對論的“質速關係”,進而動搖了狹義相對論的整體體系。
Recently, scientific researcher Xinghong Wang published an article in the field of physics studying the acceleration process of cosmic ray particles inside solar system by the gravitational field of the sun. The conclusion of this scientific research article fundamentally questions the mass-velocity relation of special relativity. It therefore shakes the entire system of special relativity.
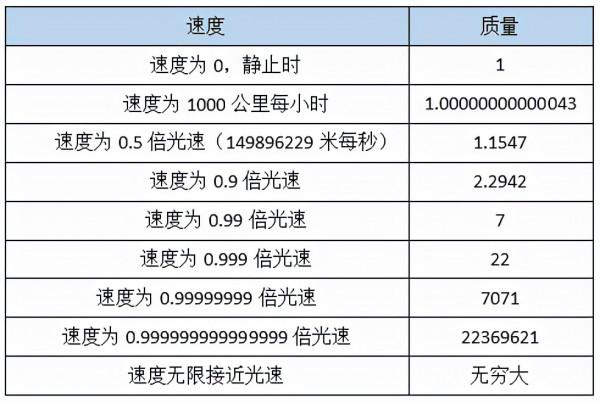
所謂“質速關係”,指的是,根據狹義相對論,物質的質量並不是一成不變的,而是隨著速度發生改變。如果一個物體在靜止時的質量是1公斤,那麼,在對其進行加速後,該物體的質量也會增加。具體速度與質量的對應關係,基本如下表所示:
The so-called "mass velocity relation" means that according to the special relativity, the mass of matter is not invariable, but changes with the speed. If the mass of an object at rest is 1 kg, the mass of the object will increase after accelerating it. The corresponding relationship between specific speed and mass is basically shown in the following table:
如上表所述的相對論“質速關係”,被現今的科學界公認為是已經過驗證的正確理論。
驗證“質速關係”的最廣為人知的證據是,目前人類的所有粒子加速器均不能將粒子加速到比光速更快的速度。當使用加速器加速粒子時,無論加速器有多強大,粒子的速度也只能無限接近光速,但永遠無法達到光速,更不用說超過光速了。因為,根據狹義相對論,當一個粒子從靜止開始加速時,它的速度增加很快,因為它的靜止質量很小,慣性很小,容易被加速;但當它的速度增加後,它的質量也增加,慣性變大,其速度增加就變慢;當該粒子被加速到接近光速時,它的質量(慣性)將變得非常巨大,因此加速力與它的質量(慣性)相比,相對來說是特別小的,可以忽略不計,所以粒子的速度的增加越來越慢,以至於接近於零。因此,它的速度將總是低於光速。
The "mass-velocity relation" of special relativity as shown in the above table is recognized by the current scientific community as a verified and correct theory. The most well-know proof of the mass and speed relationship is that current accelerators can not accelerate particles to be faster than the speed of light. When using accelerators to accelerate particles, no matter how powerful the accelerators are, the speed of the particles can only approach the speed of light but can never reach the speed of light, let alone surpassing the speed of light. Because according to special relativity "mass-velocity relation" , when a static particles is accelerated, the acceleration is very quick due to its tiny mass(tiny inertia); when the speed of the particle increases, its mass and inertia also increase, thus the acceleration becomes more difficult; When the particle is accelerated to be close to the speed of light, its mass (inertia) will become very huge, so the acceleration force is relatively extremely small and negligible compared with its mass (inertia), so the increase of particle speed becomes so slow as to be close to zero. As a result, the speed of the particle will always be lower than the speed of light.
這就好比用火車頭拉車皮,一個火車頭拉一節車皮(幾十噸),速度可以很快增加;但一個火車頭拉一千節車皮(幾萬噸),速度增加就很慢;而如果用一個火車頭拉一座大山(幾億噸),速度增加就特別小;如果用一個火車頭拉整個地球(幾十萬億億噸),那麼火車頭對地球的加速度,就可以忽略不計,火車頭拉力太小,地球質量和慣性太大,造成的速度增加微乎其微。
This is like using a locomotive to pull a wagon. If a locomotive pulls one wagon(dozens of tons), the speed can be increased quickly; But when a locomotive pulls a thousand wagons(tens of thousands of tons), the speed increases very slowly; If you use a locomotive to pull a mountain (hundreds of millions of tons), the speed increase is particularly tiny; If a locomotive is used to pull the whole earth (thousands of billions of billions of tons), the acceleration of the earth by the locomotive is negligible because the pulling force of the locomotive is too small, and the mass and inertia of the earth are too large, thus the speed increase is almost zero.
這樣來看,狹義相對論的“質速關係”,確實是有道理的。王行洪透過對高速宇宙射線進行研究,發現了“質速關係”的漏洞。
宇宙射線,是宇宙中普遍存在的高速運動的粒子,他們的普遍特點是速度極快,而且不同的宇宙射線粒子,其運動方向是隨機的。因此,可以確定,每年都有許多宇宙射線粒子以不低於99.99999999%光速的速度穿過地球軌道朝太陽運動。
From this point of view, the "mass-velocity relation" of special relativity is indeed reasonable. However, through the study of high-speed cosmic rays particles, Wang Xinghong found the problem of "mass-velocity relation".
It is a well know fact that, in the space, there are many cosmic ray particles travelling at very very high speeds and that the travelling directions of cosmic rays particles are essentially randomized. Thus, there must be many cosmic ray particles travelling through earth orbit towards the sun at speeds no lower than 99.99999999% speed of light each year.
王行洪透過研究這樣的宇宙射線粒子發現,這些粒子朝向太陽運動,所以勢必受到太陽引力的作用而引起速度增加。太陽引力對宇宙射線粒子進行加速後,由於“質速關係”,速度增加造成宇宙射線粒子質量增加,根據萬有引力定律,質量增加後的宇宙射線粒子,受到的太陽引力也同樣增加。也就是說,粒子質量(慣性)增加後,加速變得困難,但加速力也同步增加,所以加速又變得容易,正反抵消後,總體效果就是,相對論“質速關係”對這個加速過程沒有影響。
By studying such cosmic ray particles, Wang Xinghong discovered that these particles move toward the sun, so they are bound to be affected by the sun's gravitational force and, as a result, their speed will increase. After the cosmic ray particles are accelerated by the sun's gravity, the mass of the cosmic ray particles increases due to the "mass-velocity relation". According to the law of universal gravitation, the sun’s gravitational force towards the cosmic ray particles also increases. This is to say, because the particle’s mass (inertia) increases, the acceleration becomes more difficult; but the acceleration force (gravitational force) also increases simultaneously, so the acceleration becomes easier. After considering both the increase of the mass(inertia) and the increase of the acceleration force, the overall effect is that the special relativity "mass-velocity relation" has no effect on this acceleration process.
依然以火車頭拉車皮做比喻,就是說,原先是一個火車頭拉一節車皮,加速容易,後來,隨著火車皮數量的增加,變成一千節車皮,但火車頭也同樣增加,變成一千個火車頭,加速仍然容易;隨著火車皮數量再增加,變成地球那麼重(幾十萬億億噸),但火車頭數量也同等增加,變成有若干萬億億個火車頭,平均下來,一個火車頭仍然拉一節車皮,所以加速仍然同樣容易。
We can still use the analogy of locomotive pulling wagon. In the beginning, it is one locomotive pulling one wagon, so the acceleration is easy. Later, the number of wagon increases from one wagon to one thousand wagons. But the number of locomotives also increases from one locomotive to one thousand locomotives. Thus, the acceleration is still easy. Then, the number of wagons increases to be very huge.For example, the weight of total wagons are as heavy as the earth(thousands of billions of billions of tons). But the number of locomotives also increases proportionally so that there are hundred of billions of billions locomotives. On average, one locomotive still pulls one wagon, so the acceleration is still easy.
因此,在地球軌道附近,以99.99999999%光速朝向太陽運動的宇宙射線粒子,經計算,其加速度將始終不會低於5.96×10-3m/s2。
這意味著,每隔1秒後,粒子的速度將至少增加5.96×10-3米每秒。因此,當這個高速粒子向太陽移動時,它將很容易被太陽加速到無限接近光速的速度,因此,它的質量將(根據狹義相對論的“質速關係”)變得比太陽、比整個太陽系、比我們的星系甚至比整個宇宙都大得多!
Thus when we calculate a particle moving through earth orbit towards the sun, if the speed of it is 99.99999999% speed of light when at earth orbit, we can find that, according to calculation, the acceleration of the particle will always be no lower than 5.96×10-3m/s2.
This means, after every 1 second, the speed of the particle will increase by at least 5.96×10-3m/s. Thus, when it travels to the sun, the particle will be very easily accelerated by the sun to be extremely close to the speed of light so that its mass will be much bigger than the sun, the whole solar system, our galaxy, or even the whole universe.
此外,我們還可以發現,沒有什麼能阻止這個粒子進一步加速到比光速更快!因為不管它的質量有多大,它仍然會被太陽的引力吸引,並以越來越快的加速度進一步增加速度。因為它的加速度的大小與它急劇增加的質量無關。
經過計算,當它在地球軌道附近向太陽運動的過程中,最多隻需經過5.1秒,它的速度就將超過光速。
In addition, we can also find that nothing will prevent this particle from being further accelerated to be faster than the speed of light. Because no matter how huge its mass becomes, it will still be attracted by the gravity of the sun and be further accelerated at INCREASING rate. Its acceleration has nothing to do with its enormously increased mass.
As a result, the speed of this particle will surpass light speed after at most 5.1 seconds when it travels towards the sun.
具體運算過程為:因為粒子在地球軌道附近的初始速度為99.99999999%光速,光速為299792458米每秒,所以粒子的初始速度為299792458× 99.99999999%=299792457.970021米每秒。而粒子的速度至少每秒增加5.96×10-3m/s。所以,5.1秒後粒子的速度至少為:299792457.970021+5.1×5.96×10-3 =299792458.000417m/s。該速度大於光速(299792458m/s)!
The calculation process is as follows:
Because the particle’s speed(“initial speed”) is 99.99999999% light speed when near earth orbit, and the speed of light is 299792458m/s, so the “initial speed” of the particle is 299792458×99.99999999%=299792457.970021m/s. Because we already know that after every 1 second, the speed of the particle will increase by at least 5.96×10-3m/s. So, 5.1 seconds after this particle travels towards the sun, its speed will become no lower than: “initial speed” + “speed increase” =299792457.970021 +5.1×5.96×10-3=299792458.000417m/s. This is faster than speed of light!
也就說是,根據王行洪先生對高速宇宙射線在太陽引力場中加速過程的研究,如果狹義相對論是正確的,會得出兩個結論:
首先,宇宙射線粒子的質量將變得達到無窮大(遠遠超過宇宙總質量1053公斤)。這顯然是不可能的,不現實的。因為,如果這是可能和現實的,那麼,這樣的情況早就發生了。畢竟,太陽系中有很多這樣的宇宙射線,能夠滿足這樣的條件。
其次,宇宙射線粒子會被太陽持續加速,其速度將迅速超過光速。這也是與相對論的基本假設相悖的。目前,科學界普遍公認,所有粒子的速度是不可能超過光速的。
This is to say, based on Xinghong Wang’s study, if special relativity is correct, there will be two conclusions:
Firstly, before reaching the speed of light, the mass of the cosmic ray particle will become infinitely huge. It will be countless billions of times bigger than the mass of entire universe. This is apparently absurd and unrealistic and untrue. Because if it were true, it would have already happened before. But it never happened.
Secondly, this particle will be continuously accelerated to very quickly become faster than the speed of light. This is also against the basic postulate of the theory of relativity. Nowadays, it is generally accepted in the scientific community that the speed of all particles cannot exceed the speed of light.
因此,王行洪的這項研究,是可以動搖狹義相對論的“質速關係”的。由於狹義相對論“質速關係”使用了與狹義相對論“尺縮效應”和狹義相對論“鐘慢效應”相同的科學邏輯,因此“尺縮效應”和“鐘慢效應”應該也是不成立的。
Thus this study by Xinghong Wang seems sufficient to disprove the mass(momentum/energy)-velocity relation of special relativity. Because the mass(momentum/energy)-velocity relation uses the same scientific logic as that of special relativity length-shrinkage and special relativity time-dilation, length-shrinkage and time-dilation of special relativity should probably also be untrue.
王行洪的這項研究,已經發表論文,獲得科研領域的智慧財產權。他還發表過關於質疑狹義相對論“時間膨脹”等課題的相關論文。
This scientific research achievement by Xinghong Wang has already been published on international journal and owned relevant intellectual property. He has also published other articles which questions special relativity time-dilation etc.
王行洪的已發表科研成果,還包括了對於宇宙加速膨脹現象的解釋。在之前的論文中,王行洪經過計算首次提出,恆星對宇宙輻射壓力的總值,其實大於其對整個宇宙的萬有引力總和。也就說是,宇宙中全部恆星,其輻射壓力的效果是會造成宇宙膨脹,其萬有引力的效果是會造成宇宙收縮,但經過計算,總輻射壓力是大於總萬有引力的,所以,宇宙必然是加速膨脹的。計算過程並不複雜,粗略的計算證明,恆星總輻射壓力是總萬有引力數值的數倍。比較精確的計算顯示(以太陽為例),恆星總輻射壓力÷總萬有引力=6.425。即,對於太陽來說,其恆星總輻射壓力比其對宇宙的總萬有引力大5.425倍。
Moreover, Wang Xinghong's previously published scientific research achievements also include an explanation for the accelerated expansion of the universe. In his research article, Wang Xinghong first proposed through calculation that the total expansion forces caused by the radiation pressure of stars in the universe is actually larger than the total contraction force caused by gravity inside universe.
For all the stars inside universe, their radiation pressure forces cause the universe to expand, and their gravitational forces cause the universe to contract. After calculation, Xinghong Wang found that the total radiation pressure forces inside the universe are bigger than the total gravitational forces. Thus the universe must expand at accelerating rates. The calculation process is not complicated. A rough calculation proves that the total radiation pressure forces of stars are several times bigger than the total gravitational forces. A more accurate calculation taking the sun as example shows: total radiation pressure forces÷total gravitational forces=6.425. That is, for stars like the sun, their total radiation pressure forces are 5.425 times greater than their total gravitational forces towards the entire universe.
{
具體計算過程為:
Calculation process is as follows:
已知,在一個天文單位處,太陽的輻射的壓強(在陽光被全部反射的情況下)為p=9.06牛頓每平方公里。同時,以一個天文單位(1.5×108千米)為半徑r的球體的總面積為:
S=4πr²=4×3.14×1.5×108×1.5×108=2.8×1017km2
所以,太陽輻射的壓力總和為:Fpressure=p×S=2.54×1018N
We already know that the pressure exerted by sunlight on objects at 1 AU from the sun is(When the light is fully reflected): p = 9.06N/km2.
And the total area of the surface of the virtual ball with radius of 1AU is roughly: S=4πr²=4×3.14×1.5×108 ×1.5×108 =2.8×1017km2.
So the total force of pressure of sunlight Fpressure=p×S=2.54×1018N.
而在太陽整個生命週期中,包括已過去的45億年和未來的50億年為主序星階段,主序星階段後還有20億年左右的紅巨星階段,在紅巨星階段的太陽輻射為目前的3000倍。
And, the current sun is in the stage of main-sequence star of its life time with a current age of 4.5 billion years. After 5 billion years when it’s main-sequence star stage come to an end, it will become a red giant star which will last for 2 billion years with the brightness 3000 times larger than it is now.
因此,太陽整個生命週期內的總輻射壓力為:
So the average radiation pressure force of the sun throughout its life time can be roughly:
Ftotal pressure=(Fpressure×(45億+50億)+Fpressure×3000×20億)/(45億+50億+20億)
=(2.54×1018N×(45+50)+2.54×1018N×3000×20)/(45+50+20)
=(24.13×1018N+ 15240×1018N)/115=1.33×1021N
Ftotal pressure= (Fpressure × (4.5 billion years + 5 billion years) + Fpressure × 3000 × 2 billion years) / (4.5 billion years + 5 billion years + 2 billion years) = (2.54 × 1018N × (4.5+5) + 2.54 × 1018N × 3000×2) / (4.5+5+2) =1.33 × 1021N
而已知宇宙半徑為4.4x1026米,太陽質量Msun 為 2×1030kg,宇宙總質量Muniverse 為1×1053kg,所以,經過把宇宙分割成無數個以太陽為中心的球殼體(spherical shell),進行積分運算,可得,太陽對整個宇宙的萬有引力總和為:
Whereas the total mass of the sun Msun is 2×1030kg, the total mass of the universe Muniverse is 1×1053kg, and the radius of the universe R is approximately 4.4×1026m. At astronomical level, mass of the universe can be seen as evenly distributed. Thus the sun’s total gravitational pull towards the entire universe, excluding nearby galaxies, can be calculated by dividing universe into infinite numbers of 3-dimensional spherical shells like onions and then performing integral calculation to find the total value:
進行比較,發現,Ftotal pressure/Funiverse=1.33×1021N/2.067×1020N=6.425. 所以,在宇宙中,太陽這樣的恆星其總輻射壓力比總萬有引力大5.425倍。
And, Ftotal pressure/Funiverse=1.33×1021N/2.07×1020N=6.425. So, for stars like the sun, their average total radiation pressure force is 5.425 times larger than their total gravitational pulling force towards the entire universe (excluding nearby galaxies).
因為太陽本身是一箇中小質量恆星,更大質量恆星的輻射壓力將是太陽的許多倍。因此,參照相關資料後,可以發現,宇宙中總輻射壓力會比總萬有引力大更多倍。
In fact, the sun itself is a small/medium mass star, the radiation pressure of a larger mass star will be many times bigger than that of the sun. After taking into account of relevant data, it can be found that the ratio of total radiation pressure in the universe vs total gravity will be bigger than 6.425.
}
因此,即使沒有所謂“暗能量”的存在,宇宙也會因為恆星輻射壓力而加速膨脹。王行洪的這一創新性科研成果,否定了之前科學界普遍提及的“空間膨脹”理論和“暗能量”存在的基礎,對於現今的宇宙起源、發展演變過程、宇宙壽命等方面的研究,都具有重要的現實科學意義。
Therefore, even if there is no so-called "dark energy", the universe will still expand at accelerating rates because of radiation pressure forces. This innovative scientific research achievement proves that there is no foundation for the existence of "space expansion" theory and "dark energy" which were believed by many people, and has important practical and scientific significance for the research on the origin, development and evolution process and current age of the universe.
這項對於引力場中宇宙射線粒子加速過程的研究成果,已經觸及相對論理論體系的核心,動搖了相對論的“質速關係”,相信會很快得到主流科學界的承認,我們拭目以待!
For this time, the scientific research achievements about the process of cosmic ray particles being accelerated by gravitational field have touched the core of the theoretical system of special relativity and shaken the mass-velocity relation of special relativity. It is expected that this achievement will soon receive recognition and approval from the mainstream scientific community and the public.